Description

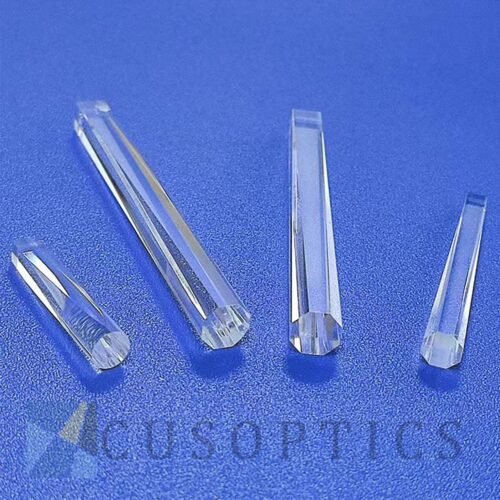
An equilateral prism is a fundamental optical prism with three 60-degree angles, making it ideal for light deviation and dispersion. Manufactured from high-quality K9 glass (or its international equivalent, BK7 optical glass), this prism offers excellent homogeneity and transmission across the visible spectrum.
The primary function of this dispersion prism is to separate white light into its constituent colors. This 60-60-60 dispersion occurs because different wavelengths of light bend at slightly different angles when passing through the glass. This property is crucial in spectroscopy for analyzing material composition.
Beyond research, its predictable light dispersion makes it a perfect tool for teaching demostrations in physics classrooms and for use in various lab equipment. It effectively illustrates fundamental principles of refraction and the nature of light. These prisms are precision polished to optical standards, ensuring reliable performance for both educational and professional applications in scientific and industrial settings.
Features:
Plano-Convex Lens (PCX): Converges light. One flat, one convex surface. Minimizes spherical aberration for collimating or focusing light. Common in laser applications.
Plano-Concave Lens (PCV): Diverges light. One flat, one concave surface. Used for beam expansion, projection, or correcting aberrations in optical systems.
Double-Convex Lens (DCX): Symmetrical converging lens. Two convex surfaces. General-purpose lens for magnification and imaging, but introduces more aberration than PCX.
Double-Concave Lens (DCV): Symmetrical diverging lens. Two concave surfaces. Used for beam expansion, image reduction, and as a simple negative lens in eyepieces.
Achromatic Doublet: Corrects chromatic aberration. A compound lens made by cementing a convex (crown glass) and a concave (flint glass) element. Essential for high-quality imaging.
Meniscus Lens: Has one convex and one concave surface. Can be positive or negative. Primarily used to minimize spherical aberration in systems like camera lenses.