Double-Convex Lens
Custom Fabrication
Custom Fabrication
Any question you want to know, just to contact email: cusoptics@micquartz.com.
What is double-convex lens?
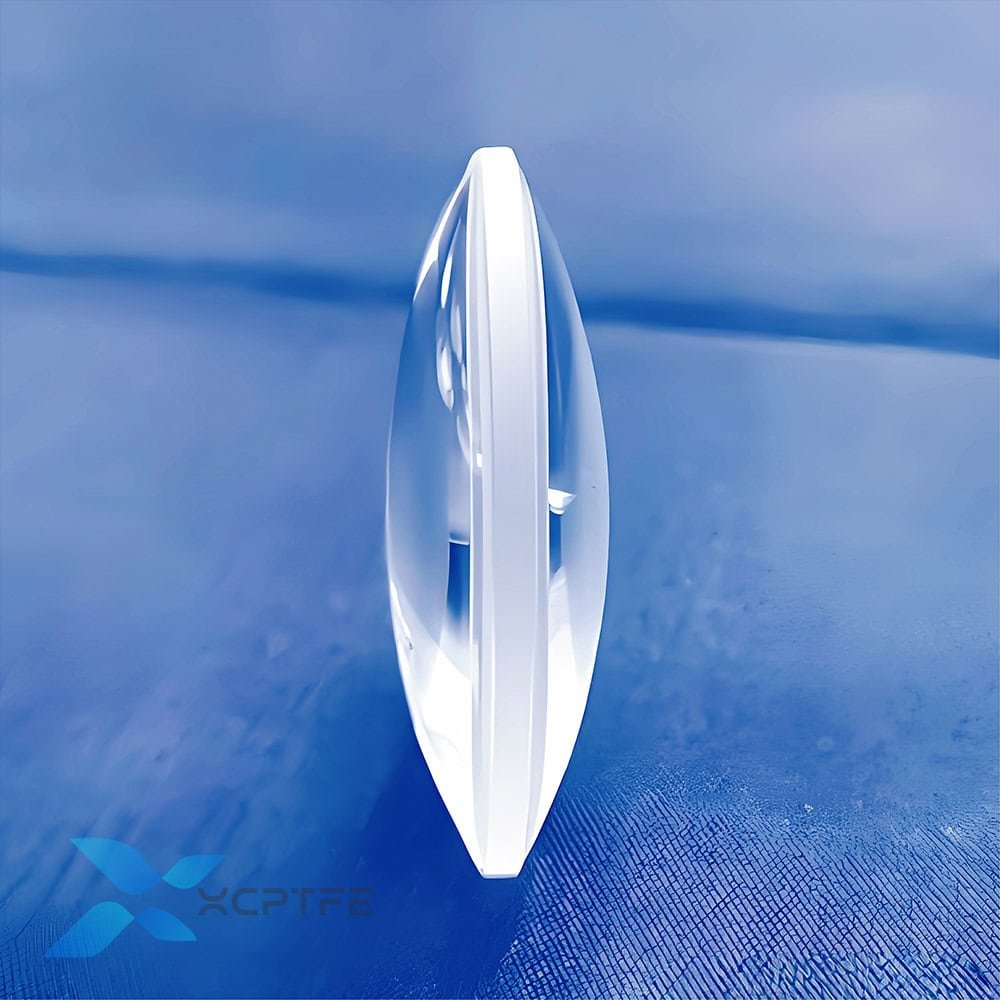
Double convex lens is a basic and common optical lens. Its name directly describes its physical shape. Both surfaces protrude outward. It is the most typical representative of converging lenses.
Features
Shape: The central part of the lens is thickest, gradually thinning towards the edges, forming a shape similar to a rugby ball (but the curvature radii of the two surfaces can be the same or different).
Optical function: converging lens. Its main function is to deflect parallel incident visible light rays towards the main optical axis, causing them to converge to a point on the other side of the lens.
Focal length: has a positive focal length (+). The focal length depends on the curvature radius of the two surfaces of the lens and the refractive index of the material used to manufacture the lens.
How does DCX Lens work?
According to the position of the object relative to the focal point of the lens, a biconvex lens can form two types of images:
Real image: When an object is located beyond the focal length of a lens, the lens can form an inverted real image on the other side that can be projected onto a screen. This is the working principle of cameras, camcorders, projectors, and eyes.
Virtual image: When an object is within one focal length of a lens, an upright, magnified virtual image will be seen through the lens. This image cannot be projected onto the screen, but it can be seen by the human eye. This is the working principle of a magnifying glass.
Application
Due to its excellent convergence and imaging capabilities, double-convex lenses are the core components of countless optical systems
Imaging system: serving as the primary objective or eyepiece for cameras, camcorders, telescopes, microscopes, and binoculars.
Magnification: Used as a simple magnifying glass.
Spotlight: Used in lighting systems to converge the light emitted by a light source (such as an LED or bulb) and form a parallel beam or focus it onto a specific area, such as the spotlight component of projectors and flashlights.
Laser optics: used for collimation, focusing laser beams, or beam adjustment in laser systems.
Advantages & Limitations
Advantages: Simple structure, relatively easy manufacturing, and good imaging quality in situations with low requirements.
Limitations: A single biconvex lens may exhibit significant aberrations, especially spherical aberration and chromatic aberration. This means that the light cannot converge perfectly to a single point, resulting in blurry images or colored edges. In high-precision optical applications, it is usually necessary to correct these aberrations by using lens groups (such as the mentioned achromatic dual lens) or adopting non spherical designs.
Send Us A Message
